 |
| Nakshtra |
| Sanskrit | Western star name | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aśvinī अश्विनी | β and γ Arietis | |||||
| 2 | Bharaṇī भरणी | 35, 39, and 41 Arietis | |||||
| 3 | Kṛttikā कृत्तिका | Pleiades | |||||
| 4 | Rohiṇī रोहिणी | Aldebaran | |||||
| 5 | Mṛgaśiras म्रृगशीर्षा | λ, φ Orionis | |||||
| 6 | Ārdrā आद्रा | Betelgeuse | |||||
| 7 | Punarvasu पुनर्वसु | Castor and Pollux | |||||
| 8 | Puṣya पुष्य | γ, δ and θ Cancri | |||||
| 9 | Aśleṣā आश्ळेषा / आश्लेषा | δ, ε, η, ρ, and σ Hydrae | |||||
| 10 | Maghā मघा | Regulus | |||||
| 11 | Pūrva or Pūrva Phalguṇī पूर्व फाल्गुनी | δ and θ Leonis | |||||
| 12 | Uttara or Uttara Phalguṇī उत्तर फाल्गुनी | Denebola | |||||
| 13 | Hasta हस्त | α, β, γ, δ and ε Corvi | |||||
| 14 | Citrā चित्रा14 | Spica | |||||
| 15 | Svāti स्वाति | Arcturus | |||||
| 16 | Viśākha विशाखा | α, β, γ and ι Librae | |||||
| 17 | Anurādhā अनुराधा | β, δ and π Scorpionis | |||||
| 18 | Jyeṣṭha ज्येष्ठा | α, σ, and τ Scorpionis | |||||
| 19 | Mūla मूल/मूळ | ε, ζ, η, θ, ι, κ, λ, μ and ν Scorpionis | |||||
| 20 | Pūrvāṣāḍha पूर्वाषाढा | δ and ε Sagittarii | |||||
| 21 | Uttarāṣāḍha उत्तराषाढा | ζ and σ Sagittarii | |||||
| 22 | Śravaṇa श्रवण | α, β and γ Aquilae | |||||
| 23 | Śraviṣṭhā or Dhaniṣṭha श्रविष्ठा or धनिष्ठा | α to δ Delphinus | |||||
| 24 | Śatabhiṣak or Śatatārakā शतभिषक् / शततारका | γ Aquarii | |||||
| 25 | Pūrva Bhādrapadā पूर्वभाद्रपदा / पूर्वप्रोष्ठपदा | α and β Pegasi | |||||
| 26 | Uttara Bhādrapadā उत्तरभाद्रपदा / उत्तरप्रोष्ठपदा | γ Pegasi and α Andromedae | |||||
| 27 | Revatī रेवती | ζ Piscium |
List of Nakshatras[edit]
The classical list of 27 nakshatras is first found in the Vedanga Jyotisha, a text dated to the final centuries BCE. The nakshatra system predates the influence of Hellenistic astronomy on vedic tradition, which became prevalent from about the 2nd century CE.
In Hindu astronomy, there was an older tradition of 28 Nakshatras which were used as celestial markers in the heavens. When these were mapped into equal divisions of the ecliptic, a division of 27 portions was adopted since that resulted in a cleaner definition of each portion (i.e. segment) subtending 13° 20' (as opposed to 12° 51 3/7’ in the case of 28 segments). In the process, the Nakshatra Abhijit was left out without a portion[3]:179. The Surya Siddhantha concisely specifies the coordinates of the twenty seven Nakshatras[3]:211
The following list of nakshatras gives the corresponding regions of sky, following Basham.[4]
| No. | Name | Associated stars | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ashvini "wife of the Ashvins" | β and γ Arietis |
|  |
| 2; 7 | Bharani "the bearer" | 35, 39, and 41 Arietis |
|  |
| 3 | Krittika an old name of the Pleiades; personified as the nurses of Kārttikeya, a son of Shiva. | Pleiades |  | |
| 4; 9 | Rohini "the red one", a name of Aldebaran. Also known as brāhmī | Aldebaran |
|  |
| 5; 3 | Mrigashīrsha "the deer's head". Also known as āgrahāyaṇī | λ, φ Orionis |  | |
| 6; 4 | Ardra "the moist one" | Betelgeuse |
|  |
| 7; 5 | Punarvasu (dual) "the two restorers of goods", also known as yamakau "the two chariots" | Castor and Pollux |
|  |
| 8; 6 | Pushya "the nourisher", also known as sidhya or tiṣya | γ, δ and θ Cancri |  | |
| 9; 7 | Āshleshā "the embrace" | δ, ε, η, ρ, and σ Hydrae |
|  |
| 10; 15 | Maghā "the bountiful" | Regulus |
|  |
| 11 | Pūrva Phalgunī "first reddish one" | δ and θ Leonis |
|  |
| 12 | Uttara Phalgunī "second reddish one" | Denebola |
|  |
| 13 | Hasta "the hand" | α, β, γ, δ and ε Corvi |  | |
| 14 | Chitra "the bright one", a name of Spica | Spica |
|  |
| 15 | Svāti "Su-Ati (sanskrit) Very good" name of Arcturus | Arcturus |
| 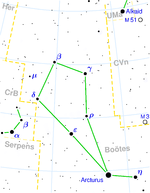 |
| 16; 14 | Visakha "forked, having branches"; also known as rādhā "the gift" | α, β, γ and ι Librae |  | |
| 17 | Anuradha "following rādhā" | β, δ and π Scorpionis |
|  |
| 18; 16 | Jyeshtha "the eldest, most excellent" | α, σ, and τ Scorpionis |
| 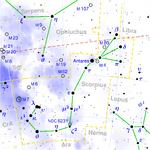 |
| 19; 17 | Mula "the root" | ε, ζ, η, θ, ι, κ, λ, μ and νScorpionis |
|  |
| 20; 18 | Purva Ashadha "first of the aṣāḍhā", aṣāḍhā "the invincible one" being the name of a constellation | δ and ε Sagittarii |
|  |
| 21 | Uttara Ashadha "second of the aṣāḍhā" | ζ and σ Sagittarii |
|  |
| 22; 20 | Abhijit "victorious"[5] | α, ε and ζ Lyrae - Vega | Lord: Brahma | |
| 23; 20 | Sravana | α, β and γ Aquilae |
|  |
| 24; 21; 23 | Dhanishta "most famous", also Shravishthā "swiftest" | α to δ Delphini |
|  |
| 24; 22 | Shatabhisha "requiring a hundred physicians" | γ Aquarii |
|  |
| 25; 3 | Purva Bhadrapada "the first of the blessed feet" | α and β Pegasi |
|  |
| 26; 4 | Uttara Bhādrapadā "the second of the blessed feet" | γ Pegasi and α Andromedae |
|  |
| 27; 5 | Revati "prosperous" | ζ Piscium |
|  |
Padas (quarters)[edit]
The 27 Nakshatras cover 13°20’ of the ecliptic each. Each Nakshatra is also divided into quarters or padas of 3°20’, and the below table lists the appropriate starting sound to name the child. The 27 nakshatras, each with 4 padas, give 108, which is the number of beads in a japa mala, indicating all the elements (ansh) of Vishnu:
| # | Name | Pada 1 | Pada 2 | Pada 3 | Pada 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ashwini (अश्विनि) | चु Chu | चे Che | चो Cho | ला La |
| 2 | Bharani (भरणी) | ली Li | लू Lu | ले Le | लो Lo |
| 3 | Kritika (कृत्तिका) | अ A | ई I | उ U | ए E |
| 4 | Rohini(रोहिणी) | ओ O | वा Va/Ba | वी Vi/Bi | वु Vu/Bu |
| 5 | Mrigashīrsha(म्रृगशीर्षा) | वे Ve/Be | वो Vo/Bo | का Ka | की Ke |
| 6 | Ārdrā (आर्द्रा) | कु Ku | घ Gha | ङ Ng/Na | छ Chha |
| 7 | Punarvasu (पुनर्वसु) | के Ke | को Ko | हा Ha | ही Hi |
| 8 | Pushya (पुष्य) | हु Hu | हे He | हो Ho | ड Da |
| 9 | Āshleshā (आश्लेषा) | डी Di | डू Du | डे De | डो Do |
| 10 | Maghā (मघा) | मा Ma | मी Mi | मू Mu | मे Me |
| 11 | Pūrva or Pūrva Phalgunī (पूर्व फाल्गुनी) | नो Mo | टा Ta | टी Ti | टू Tu |
| 12 | Uttara or Uttara Phalgunī (उत्तर फाल्गुनी) | टे Te | टो To | पा Pa | पी Pi |
| 13 | Hasta (हस्त) | पू Pu | ष Sha | ण Na | ठ Tha |
| 14 | Chitra (चित्रा) | पे Pe | पो Po | रा Ra | री Ri |
| 15 | Svātī (स्वाति) | रू Ru | रे Re | रो Ro | ता Ta |
| 16 | Viśākhā (विशाखा) | ती Ti | तू Tu | ते Te | तो To |
| 17 | Anurādhā (अनुराधा) | ना Na | नी Ni | नू Nu | ने Ne |
| 18 | Jyeshtha (ज्येष्ठा) | नो No | या Ya | यी Yi | यू Yu |
| 19 | Mula (मूल) | ये Ye | यो Yo | भा Bha | भी Bhi |
| 20 | Pūrva Ashādhā (पूर्वाषाढ़ा) | भू Bhu | धा Dha | फा Bha/Pha | ढा Dha |
| 21 | Uttara Aṣāḍhā (उत्तराषाढ़ा) | भे Bhe | भो Bho | जा Ja | जी Ji |
| 22 | Śrāvaṇa (श्रावण) | खी Ju/Khi | खू Je/Khu | खे Jo/Khe | खो Gha/Kho |
| 23 | Śrāviṣṭha (श्रविष्ठा) or Dhanishta | गा Ga | गी Gi | गु Gu | गे Ge |
| 24 | Shatabhisha (शतभिषा)or Śatataraka | गो Go | सा Sa | सी Si | सू Su |
| 25 | Pūrva Bhādrapadā (पूर्वभाद्रपदा) | से Se | सो So | दा Da | दी Di |
| 26 | Uttara Bhādrapadā (उत्तरभाद्रपदा) | दू Du | थ Tha | झ Jha | ञ Da/Tra |
| 27 | Revati (रेवती) | दे De | दो Do | च Cha | ची Chi |

No comments:
Post a Comment